Notes to a video lecture on http://www.unizor.com
Definition of Mechanical Work
Why do we apply a force to an object?
Usually, to achieve certain result, like to accelerate it to a certain speed or to move it from one point to another.
Straight line motion with a force acting along a trajectory
Consider an acceleration of a car by pressing the gas pedal. As a
result, a car will reach certain speed and then, in absence of the
traffic lights, disregarding friction and air resistance, it goes by
inertia, maintaining this constant speed.
A car with a more powerful engine will need a shorter distance to reach
certain speed. A car with a weaker engine accelerates on a longer
distance to reach the same speed.
It seems, there is some relationship between the force, the distance it
is applied to an object and the final speed reached by this object as a
result of the acting force.
Let's consider the final speed of a constant force F acting on an object of mass m, initially at rest, acting on certain distance S.
The acceleration of this object, according to the Second Newton's Law is
a = F/m
The time t to cover distance S with acceleration a is based on the formula of Kinematics
S = a·t²/2 and is equal to
t = √2S/a = √2S·m/F
From this we derive the final speed at the end of acceleration
V = a·t = (F/m)·√2S·m/F =
= √2F·S/m
As we see, the final speed of an object of mass m depends on the product of the force and the distance this force is acting.
This product that characterizes the result of applying a force on a certain distance is called the work performed by a given force acting on a given distance:
W = F·S
We can reduce by half the force and double the distance - the resulting speed will be the same.
Using this definition of work, we can represent the final speed as
V = √2W/m
Resolving for work as a function of final speed, we obtain
W = m·V²/2
So, given a final speed, we can determine how much work it takes to
achieve it and, given amount of work, we can calculate the speed this
work will cause.
This concept of work is closely tied with such less precisely
defined concepts of result, purpose, effect etc. While we not always can
compare the results or effect of two physical experiments, we can
always compare the work done by the forces participating in these experiments.
Thus, the work can be used to measure the results or effect of physical experiment.
Straight line motion with a force acting at an angle to a trajectory
Consider a slightly more complicated example with force acting at an angle to a trajectory.
A toy train of mass m is pulled by a child, who stands on a side of a track, with a constant force F, so the force acts at an angle to a straight line trajectory, making an angle φ with it.
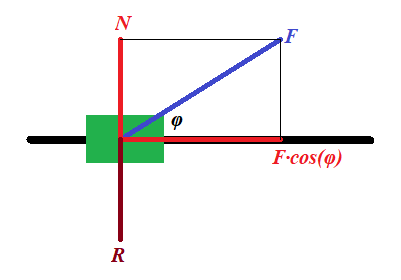
Representing this force F (in blue on a picture above) as a
sum of two forces (in red), one acting along a track, forcing the train
to speed up, and another acting perpendicularly to a track (force N), which is balanced by the reaction of the track R (in brown), we see that the force that pushes a train forward equals to F·cos(φ), while the force acting perpendicularly to a track can be simply ignored as being balanced by an opposite reaction force.
Exactly the same considerations as above leads us to a more universal formula for relationship between the final speed and the work:
V = √2W/m ,
where W = F·S·cos(φ)
Obviously, if the force acts along a straight line of a trajectory, angle φ is zero, its cosine is 1 and the formula corresponds to the one derived earlier.
Resolving the formula above for work, we obtain
W = m·V²/2
which indicates that the work depends on the result of an action
only (final speed), not the way how we achieve this result, using a
stronger force on a shorter distance or a weaker force on a longer
distance.
Motion against gravity along an inclined plane
Let's consider a completely different goal of a physical experiment and show the importance of a concept of work.
This time our purpose is to lift an object of mass m to a certain height H above the ground along a frictionless inclined plane making angle φ with horizon.
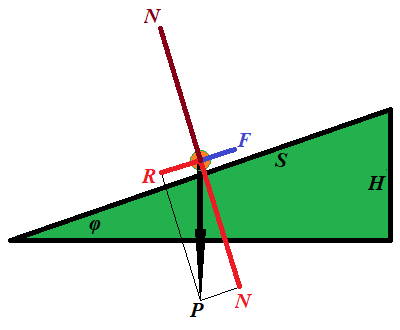
The force F needed for this must be equal to a component R of the weight P of an object along the inclined because the other component of its weight N, perpendicular to an inclined, is balanced by a reaction of the plane.
F = P·sin(φ)
The distance S this force is acting on equals to
S = H/sin(φ)
From this we can derive the work performed by force F along the distance S:
W = F·S = P·sin(φ)·H/sin(φ) =
= P·H
This is quite a remarkable result. The work does not depend on the angle of an incline, only on the height we lift the object and its weight.
As in the previous cases, the work seems to be a characteristic
of the result and does not depend on how we have achieved it, using an
inclined with bigger or smaller slope.
Rotational motion with a force acting tangentially to a trajectory
Our final example is about rotation.
Consider a person starts rotating a carousel of a radius r, having a moment of inertia I, from the state of rest to some angular speed ω with constant angular acceleration α, applying constant force F tangentially to the carousel's rim.
From the rotational dynamics we can determine angular acceleration, knowing torque τ of the force and a moment of inertia of a carousel I:
τ = F·r = I·α
α = F·r/I
Linear acceleration of the point of application of the force equals to r·α.
To achieve the final angular speed ω with angular acceleration α we need time
t = ω/α = ω·I/(F·r)
During this time the point of application of force travels around a circle for a distance of
S = r·α·t²/2 =
= r·(F·r/I)·[ω·I/(F·r)]²/2 =
= I·ω²/(2F)
Multiplying by F both sides, we obtain the relationship between work W=F·S and final angular speed achieved as a result of application of the force:
W = F·S = I·ω²/2
This is a rotational equivalent of the analogous formula for straight line movement derived in the beginning of this lecture.
So, given a final angular speed, we can determine how much work it takes
to achieve it and, given amount of work, we can calculate the angular
speed this work will cause.
Definition of work in simple cases presented above
All the above examples provide a proper basis for the following definition of the work:
Work of the force F acting at an angle φ to trajectory on the distance S is
General case of a motion along a curved trajectory
To be more precise and to cover a case of a curved trajectory, we have
to require that this definition should be applied to infinitesimal
amount of work dW performed on infinitesimal interval dS of trajectory:
dW = F·dS·cos(φ)
Using a concept of scalar product of vectors and considering force and interval as vectors, the same definition can be written as
dW = (F ·dS )
The latter represents the most rigorous definition of work.


No comments:
Post a Comment